Pathology
- With the same mechanism that would rupture an ACL or PCL in an adult (twisting on a semiflexed knee, hyperextension), in the skeletally immature can result in a tibial spine avulsion fracture
Symptoms
- Similar to ACL rupture:
- Swelling (may well have a haemarthrosis)
- Reduced range of motion
- Pain
- Difficulty weightbearing
- Feeling of or actual instability
- Positive Lachman’s test
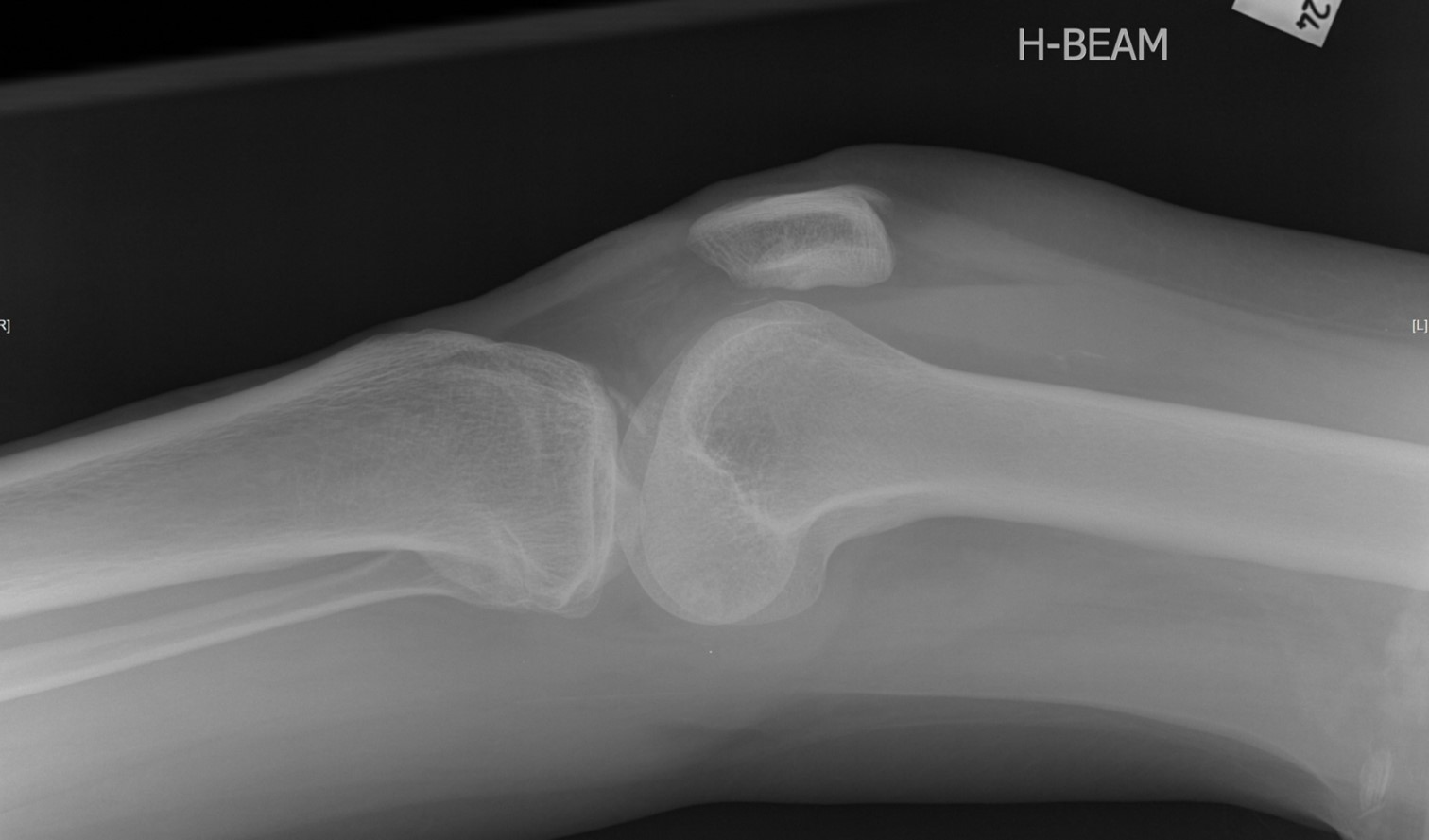
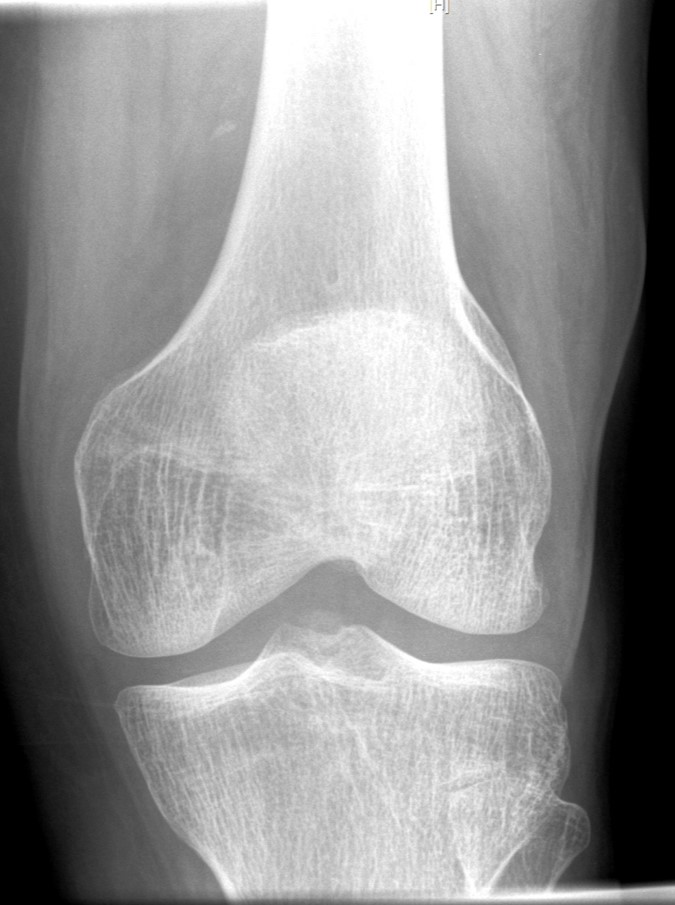
- X-ray findings
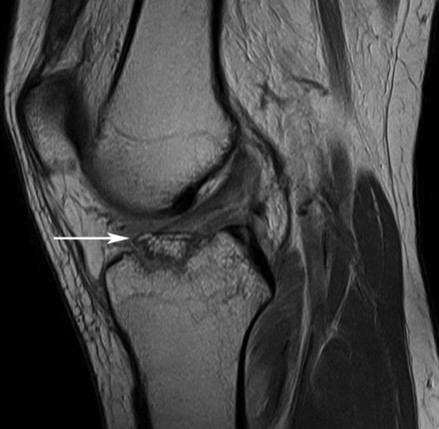
- Often small sliver of bone displaced from the tibial spine (which is often significantly more impressive on CT / MRI)
- May have a lipohaemarthrosis (as it is an intra-articular fracture)
- Often small sliver of bone displaced from the tibial spine (which is often significantly more impressive on CT / MRI)
Management
- Displaced fractures require prompt surgical management, so if suspicious of cruciate ligament injury in a child, need to x-ray
- Undisplaced fractures may be managed non-operatively, with a period of splinting and restricted activity
